Types of Microscopes
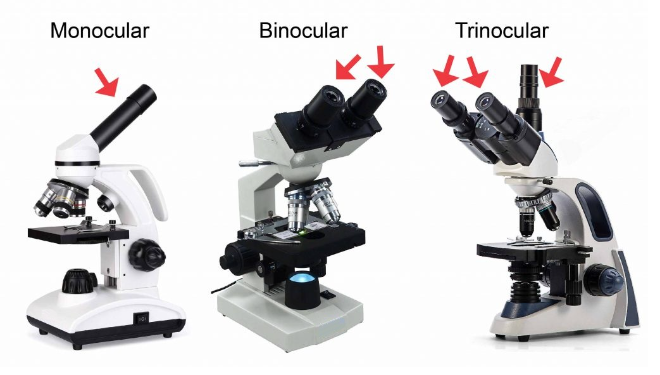
A monocular, binocular and trinocular Microscope:
A monocular microscope has a single eyepiece for viewing the specimen. Unlike binocular or trinocular microscopes, which have two or three eyepieces respectively, a monocular microscope is designed for use with one eye at a time. Monocular microscopes are generally smaller and less expensive than binocular or trinocular microscopes, making them a popular choice for hobbyists and students.
Despite having only one eyepiece, a monocular microscope still uses multiple lenses to magnify the specimen and provide a clear and detailed image. The lenses are arranged in a series along the body of the microscope, with each lens contributing to the total magnification of the image. Monocular microscopes typically have a range of magnification options, allowing users to view the specimen at different levels of detail.
A binocular microscope has two eyepieces, allowing two eyes to view the specimen simultaneously. This produces a brighter image and makes it more comfortable to observe the specimen for extended periods. Binocular microscopes are generally less expensive than trinocular microscopes.
A trinocular microscope also has two eyepieces, with an additional port that allows for the attachment of a camera or other imaging equipment. This third port is typically located above the two eyepieces and allows for simultaneous viewing through the eyepieces and imaging of the specimen. This makes trinocular microscopes useful for capturing images or videos of the specimen for documentation or further analysis.
Biological microscopes
The biological microscope is a type of microscope that is used to study small and thin specimens such as cells, bacteria, and other microscopic organisms. It uses backlight illumination (either brightfield or darkfield), with a series of lenses to magnify the specimen. The primary objective lens is located near the specimen, and the eyepiece lens is located near the observer's eye.
Biological microscopes typically have a magnification range from 40x to 1000x, and are used in many fields of science, including biology, medicine, and microbiology. Some biological microscopes are equipped with additional features such as a condenser lens, which focuses and directs light onto the specimen to improve image clarity, and a diaphragm, which regulates the amount of light entering the microscope.
To use a biological microscope, the specimen is placed on a slide and positioned under the objective lens. The observer then adjusts the focus and the magnification to view the specimen at the desired level of detail. The image is viewed through the eyepiece lens, and can also be captured using a camera or other imaging device.

Digital Microscope:
A digital microscope uses a digital camera to capture images of an object, displaying them to a screen or PC.
Digital microscopes are popular in fields such as biology, pathology, and material science, where detailed examination of specimens is necessary. They are also used in education and research, allowing students and scientists to view and analyze specimens with greater detail and precision.
Digital microscopes offer several advantages over traditional microscopes. For example, digital microscopes can capture and store images and videos of the specimen, which can be shared with others or used for further analysis. They also often have built-in software that allows for measurements and annotations to be made directly on the digital image.
Another advantage of digital microscopes is that they can be more comfortable to use for extended periods, as they do not require the user to look through eyepieces. Instead, the image is displayed on a screen, reducing eye strain and allowing for a more natural posture during use.
Overall, digital microscopes are a powerful tool for scientific observation and analysis, offering a range of features and benefits that traditional microscopes cannot match.
Digital microscopes have several features that make them useful tools for scientific observation and analysis. Some of the main features of digital microscopes include:
Image and video capture: Digital microscopes can capture and store images and videos of the specimen, which can be used for further analysis, shared with others, or used for documentation.
Digital Zoom: Digital microscopes often have a range of magnification and digital zoom options, allowing users to view the object much closer.
Image processing and analysis: Digital microscopes often come with built-in software that allows for measurements and annotations to be made directly on the digital image. Some digital microscopes also have advanced image processing and analysis capabilities, such as image stitching, 3D reconstruction, and fluorescence imaging.
Ergonomic design: Digital microscopes are often designed for comfortable use over extended periods. They may have other ergonomic features to improve usability.
Overall, the combination of digital image capture, image processing, and analysis tools make digital microscopes valuable tools for many industries.

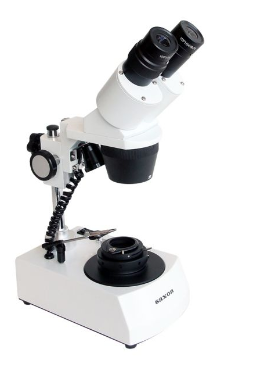
STEREO MICROSCOPE:
A stereo microscope, also known as a stereoscopic microscope or dissecting microscope, is a type of microscope that uses two separate optical paths to provide a three-dimensional view of a specimen.
Unlike a compound microscope, which uses a single optical path and produces a two-dimensional image, a stereo microscope uses two objective lenses and two eyepieces to provide a magnified, three-dimensional view of the specimen. This allows users to see the specimen in greater detail and to observe its depth and texture.
HOW TO USE STEREO MICROSCOPE?
Stereo microscopes are commonly used in fields such as biology, geology, electronics, and manufacturing, where a three-dimensional view of the specimen is necessary for analysis or inspection. They are also popular among hobbyists, such as coin collectors and naturalists, who use them to examine specimens in greater detail.
Stereo microscopes are available in a range of magnifications, from low power (typically 5x-10x) to high power (up to 100x), and they can be equipped with various accessories, such as lights and cameras, to enhance their functionality.
Stereo microscopes are used in a wide variety of applications, including biology, geology, electronics, and manufacturing. Here are the general steps for using a stereo microscope:
Overall, the exact steps for using a stereo microscope will depend on your application and the specific features of your microscope. However, by following these general guidelines, you should be able to use a stereo microscope effectively for a wide range of tasks.

BEST USAGE OF STEREO MICROSCOPE
Stereo microscopes are versatile instruments that can be used in a wide range of applications. Here are some of the best uses for a stereo microscope:
- Biological research: Stereo microscopes are commonly used in biological research to study living organisms and tissues. They are especially useful for examining larger specimens, such as insects, plants, and small animals.
- Industrial inspection: Stereo microscopes are widely used in manufacturing and industry for inspecting and manipulating small components, such as electronic circuits and mechanical parts. They can also be used for quality control and defect analysis.
- Jewelry and gemology: Stereo microscopes are used in jewelry making and gemology to examine and analyze precious stones and metals. They can be used to identify flaws, assess quality, and make precise measurements.
- Education: Stereo microscopes are often used in science education, especially at the high school and tertiary level. They allow students to observe specimens in three dimensions and to learn about anatomy, biology, and other scientific fields.
- Forensic science: Stereo microscopes are used in forensic science to examine evidence such as hair, fibers, and soil samples. They can help investigators identify suspects and determine the cause of a crime.
Overall, the best use for a stereo microscope will depend on your specific application and needs. However, the versatility and flexibility of these instruments make them useful in a wide range of scientific, industrial, and educational contexts.

Gemological Microscope:
A gemological microscope is a specialized type of microscope that is designed specifically for examining gemstones and other precious minerals. It is used by gemologists, jewelers, and other professionals who work with gems to evaluate the quality, authenticity, and characteristics of different stones.
Gemological microscopes are typically equipped with a range of features and tools that allow for detailed examination of gemstones. These may include polarizers, darkfield illumination, and magnification options ranging from 10x to 40x or higher.
Gemologists use gemological microscopes to examine a range of features of gemstones, such as inclusions (internal flaws or irregularities), color, transparency, and cut. They may also use the microscope to examine the surface of the stone for scratches or other signs of wear.
Gemological microscopes may be used in a variety of settings, including gemstone laboratories, jewelry stores, and other settings where gemstones are evaluated and appraised. They are an essential tool for anyone working with gemstones, as they allow for precise and accurate analysis of these precious materials.
Usage of Gemological Microscope:
Here are some specific ways in which a gemological microscope may be used:
Identification: A gemological microscope can help identify different types of gemstones based on their physical and optical properties. Gemologists can use the microscope to examine the stone's color, transparency, refractive index, and other features to determine what type of gemstone it is.
Quality evaluation: Gemologists use the microscope to evaluate the quality of a gemstone based on its cut, clarity, and other factors. They may use the microscope to examine the stone for inclusions or other flaws that could affect its value.
Grading: Gemological microscopes are used to grade diamonds and other gemstones based on their clarity and other characteristics. Gemologists can use the microscope to view the stone at different magnifications and determine its overall quality.
Appraisals: Jewelry appraisers may use gemological microscopes to evaluate the value of a piece of jewelry. They can examine the gemstones in the piece and evaluate their quality and rarity to determine the overall value of the piece.
Research: Gemological microscopes are also used in research settings to study the properties and characteristics of gemstones. Researchers may use the microscope to examine the crystal structure of a gemstone or to study how light interacts with different types of gemstones.
Overall, the gemological microscope is a versatile tool that is essential for anyone working with gemstones. It allows for precise and accurate analysis of these precious materials, which is crucial for identifying, grading, and appraising gemstones.
Biosecurity inspection microscopes
Biosecurity inspection microscopes have several features that make them ideal for this type of work. They often have a range of magnification options, from low to high power, to allow for detailed examination of samples at different levels of magnification. They may also include specialized illumination options, such as fluorescence or phase contrast imaging, to enhance the visualization of specific biological components.
Other features that may be included in a biosecurity inspection microscope include:
- A binocular or trinocular viewing head for comfortable viewing and the ability to take photographs or videos of samples
- High-quality optics and coatings to ensure clear, crisp images
- Ergonomic design for comfortable use during long periods of time
- Adjustable height and focus controls for precise specimen positioning and focusing
- An integrated camera or imaging system for capturing images and videos of samples
USAGE
Biosecurity inspection microscopes are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Pathogen detection and surveillance
- GMO screening and analysis
- Quarantine and border inspections
- Research and development in biodefense and biosafety
- Environmental monitoring and quality control in food and water safety
- In summary, biosecurity inspection microscopes are powerful tools that play an important role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and other biosecurity threats, as well as in identifying and characterizing new or emerging biological agents.












